To ensure accurate measurement of enzyme performance, standardized assay methods are essential. This page breaks down the most common techniques used to evaluate enzyme activity, helping manufacturers and formulators understand how enzyme potency is tested and verified.
To learn more about the enzymes we supply and their applications, visit our enzyme supplier page
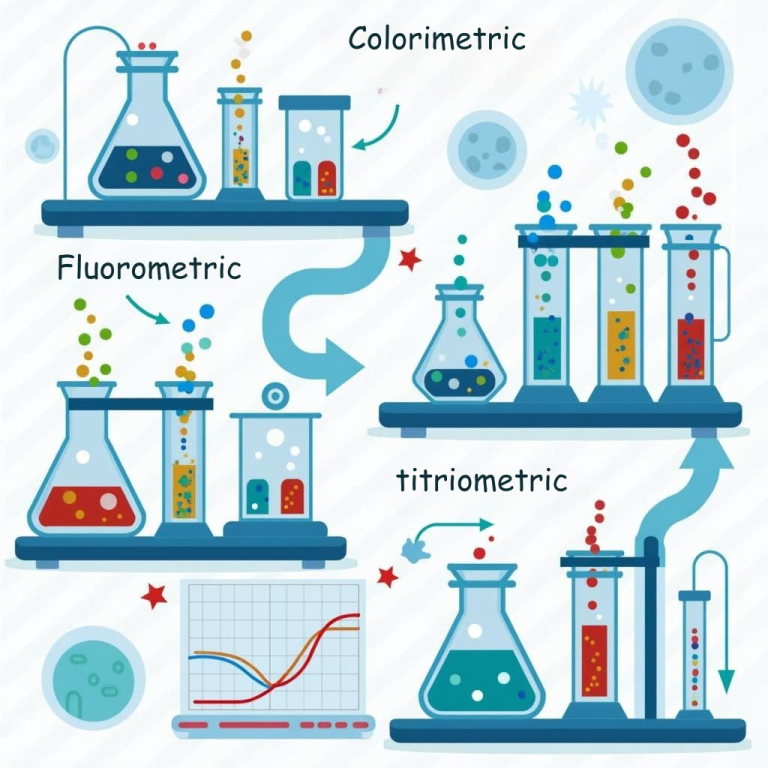
An enzyme assay is a laboratory procedure used to measure the catalytic activity of an enzyme. It determines how effectively the enzyme converts substrate into product under defined conditions.
Assays are typically designed based on the enzyme type, substrate, pH, temperature, and desired detection method.
Understanding these assay methods helps you evaluate enzyme quality and potency better. For a broader overview of enzyme activity and specifications, see our [Enzyme Activity & Technical Specifications] page.
Example –
Example –
Example –
Standardization ensures reproducibility and valid comparison between suppliers.
Different enzymes require different substrate systems:
Each method is tailored to the enzyme’s mode of action. Want a side-by-side comparison of the top enzyme assay methods? Read this blog on colorimetric vs fluorometric vs titrimetric assays.
A reliable enzyme supplier must:
At Antozyme, every enzyme batch is tested with an appropriate method to confirm –
See how activity data is reported → Enzyme Activity & Specifications
Learn more about our capabilities → Enzyme Supplier in India
Q1. What are the most common methods used to measure enzyme activity?
Ans – The most common methods include colorimetric assays, titrimetric assays, and fluorometric assays. Each method detects enzyme activity through different principles such as color change, titrant volume, or fluorescence intensity, and is chosen based on the enzyme type and application.
Q2. How is enzyme activity expressed and what do the units mean?
Ans – Enzyme activity is typically expressed in units (U), where one unit represents the amount of enzyme converting 1 micromole of substrate per minute under specified conditions. International Units (IU) are also commonly used and equivalent to U.
Q3. Why are enzyme assays important for quality control in industrial enzymes?
Ans – Enzyme assays ensure that each batch of enzyme meets required activity standards for consistent performance, optimal dosage, and cost-efficiency in industrial applications.
Q4. What factors can affect the accuracy of enzyme activity assays?
Ans – Factors such as temperature, pH, substrate concentration, incubation time, and the presence of inhibitors or cofactors can influence assay results and must be carefully controlled.
Q5. Can enzyme activity assay results vary between different laboratories?
Ans – Yes, variations in assay protocols, equipment, and conditions can cause differences in results. Standardization and validation of assay methods are essential for reliable comparisons.
Q6. Are enzyme activity assays performed in-house or outsourced to third parties?
Ans – Both options are common. Many suppliers perform in-house assays for routine quality checks, while third-party labs may be used for validation or regulatory compliance.